The way we develop websites has shifted substantially in recent years. Cloud computing is at the center of this change. According to Flexera’s 2024 State of the Cloud report, 94% of companies now use cloud services. This shift has impacted industries across the globe, including web development.
Cloud computing and web development used to be separate conversations. Not anymore. In 2025, every modern website, app, and digital service is expected to scale, update in real-time, and stay secure without downtime. None of that happens without cloud infrastructure behind the scenes.
If you’re building on the web and ignoring the cloud, you’re building slow, expensive, and outdated. This blog breaks down exactly why cloud computing matters so much for today’s web development, with examples, risks, use cases, and a look ahead.
What Is Cloud Computing in Web Development?
Cloud computing refers to delivering computing services, like storage, servers, databases, and software, over the internet instead of your local system. In the context of web development, it means deploying, scaling, and maintaining web applications using remote servers instead of owning and maintaining physical ones.
That’s the short version. In practice, this shift has changed how dev teams operate. You don’t wait for hardware or sysadmins anymore. You spin up a server in seconds, run a test, deploy globally, monitor usage in real time — all from one dashboard.
This is why the conversation around cloud computing and web development has become inseparable. They’re not competing disciplines. They’re partners.
Why Cloud Matters in Modern Web Development?
Let’s skip the fluff and get into the real reasons businesses are moving their web stack to the cloud:
- Speed to market: You can launch features faster with automated deployments, serverless environments, and real-time integrations.
- Global scale: Serving traffic from multiple continents is now as easy as changing a config file.
- Lower upfront cost: No need to invest in physical servers or dedicated IT maintenance.
- Disaster recovery: Built-in redundancy protects your app and data.
- Security updates: Cloud providers push patches automatically, helping you stay compliant.
The best part? This applies whether you’re a small SaaS or an enterprise dev team. The cloud scales with you, up or down.
Real-World Examples of Cloud-Based Web Apps
Need proof that cloud-powered web development is the norm now? Look at who’s doing it:
- Netflix: Uses AWS to dynamically scale video delivery based on demand.
- Spotify: Leverages Google Cloud to handle personalized playlists and massive user analytics.
- Slack: Runs on AWS infrastructure for global reliability and real-time communication.
- Airbnb: Uses a combination of Amazon EC2 and cloud-native data pipelines to handle search, booking, and fraud detection.
Each of these is a cloud-based web application example that started as a scrappy dev project and became global-scale thanks to the flexibility of the cloud.
Difference Between Cloud Computing and Web Development
Let’s clear something up: web development is the process of building, testing, designing websites and apps. Cloud computing is the infrastructure and backend — how those apps are deployed, scaled, secured, and monitored.
Here’s how they break down:
| Function | Web Development | Cloud Computing |
| Focus | Code, design, front-end, backend logic | Hosting, scaling, data management |
| Tools | HTML, CSS, JS, React, Node.js | AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, Kubernetes |
| Outcome | Application or site | Infrastructure to support deployment |
| Skillset | Developer / Designer | DevOps / Cloud Engineer |
You need both. It’s not cloud computing vs web development — it’s how one supports the other.
Core Service Models You Need to Know: IaaS, PaaS, SaaS
When you hear about cloud models, you’ll often come across three main types:
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
PaaS (Platform as a Service)
SaaS (Software as a Service)
These models shape your dev strategy. Many developers start with PaaS for speed, then move to IaaS as control needs grow.
AI, Edge Computing, and Where the Cloud Is Headed
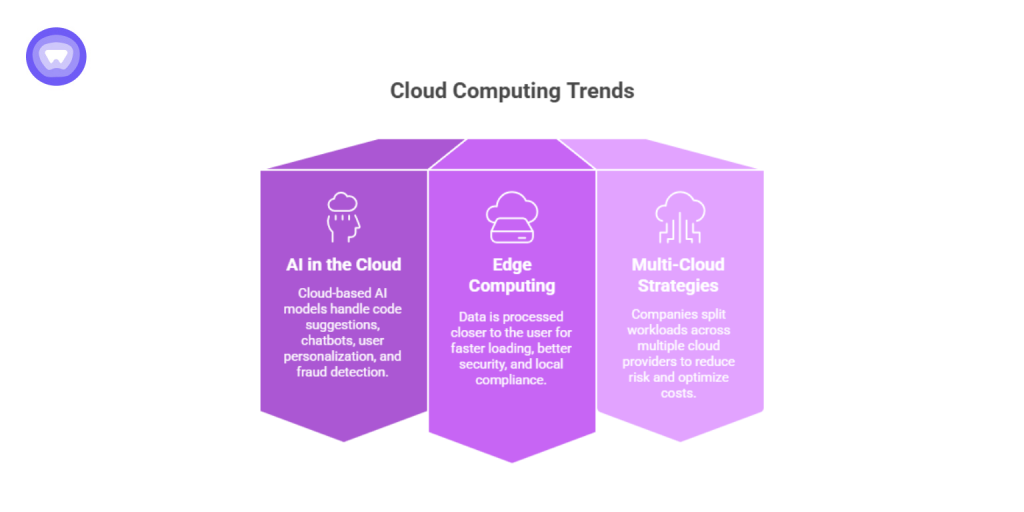
Let’s talk about trends shaping web development and cloud computing in 2025:
- AI in the cloud: Code suggestions, chatbots, user personalization, fraud detection — all handled by cloud-based AI models.
- Edge computing: Instead of sending data to central servers, data is processed closer to the user. Think faster loading, better security, and local compliance.
- Multi-cloud strategies: Companies now split workloads across AWS, Azure, and GCP to reduce risk and optimize costs.
If you’re building anything modern, ignoring these trends puts you two steps behind.
Migrating Web Development to the Cloud: A Step-by-Step Guide
You don’t need to be a CTO to start using cloud infrastructure. Here’s a high-level checklist:
- Audit your stack: What parts of your app are local or hosted on shared hosting?
- Pick your cloud provider: AWS for flexibility, Google Cloud for AI tools, Azure for enterprise compatibility.
- Choose service model: PaaS if you want speed, IaaS if you need control.
- Containerize your app: Use Docker to make your app portable.
- Set up CI/CD: Automate testing and deployment with tools like GitHub Actions or Jenkins.
- Implement monitoring: Use services like Datadog or AWS CloudWatch.
- Plan for scale: Use auto-scaling and redundancy zones.
Common Mistakes in Cloud Web Dev (And How to Avoid Them)
Lifting and shifting without optimizing
Simply uploading your legacy app to a cloud VM doesn’t work. Refactor for the cloud.
Ignoring cost controls
Cloud costs can spiral fast. Use budgets, alerts, and billing dashboards.
No disaster recovery
Always back up databases. Always test failover.
Overengineering too soon
Start simple. Don’t adopt Kubernetes unless you need it.
Estimated Monthly Costs
| Provider | Estimated Cost |
|---|
At-a-Glance Comparison: Traditional Hosting vs Cloud Hosting
| Feature | Traditional Hosting | Cloud Hosting |
| Scale | Fixed | Elastic on demand |
| Cost | Monthly fixed | Pay-per-use |
| Maintenance | Manual | Auto-patched |
| Redundancy | Limited | Global failover |
| DevOps Tools | Minimal | Built-in |
This table explains why cloud computing and web development are now often discussed together.
Why Cloud Security, Compliance, and Performance Matter?
In B2B settings, this goes beyond tech. Cloud performance affects your SLAs. Cloud security affects trust. And cloud compliance (GDPR, SOC 2) affects your ability to land enterprise clients.
You can’t bolt these on later. They need to be part of your cloud planning from the start.
PureVPN Handles Compliance, Uptime, and Scale — So You Don’t Have To
If you’re building SaaS tools, dashboards, or secure client portals — and want to layer in VPN protection, PureVPN’s White Label solution is cloud-native, privacy-first, and built for resellers.
You get:
- A cloud-hosted infrastructure with 7,000+ servers in 140+ countries
- Fully branded apps with your logo and interface
- End-to-end encryption with GDPR and SOC 2-ready architecture
- A reseller dashboard to manage users, pricing, and subscriptions
- No servers to manage, no code to write
PureVPN handles all infrastructure, updates, compliance, and maintenance. You focus on growing your brand.
If you’re in the business of building tools for others — or planning to — there’s zero reason to build VPN architecture from scratch. You resell under your own brand, and we run the cloud part for you.
1. Do you currently use any cloud provider (AWS, Azure, GCP)?
2. Do you use CI/CD tools like GitHub Actions, Jenkins, or Bitbucket Pipelines?
3. Can your stack auto-scale based on traffic or usage?
Final Thoughts
Cloud computing and web development aren’t separate decisions anymore. They’re two parts of the same strategy. Whether you’re launching a B2B SaaS, redesigning your company’s portal, or just learning where to start, the cloud is no longer optional.
The winners in 2025? Teams that build fast, scale effortlessly, and deploy securely. All of that starts in the cloud.


