The internet just witnessed its largest Google Gmail data breach to date, 183 million accounts stolen by infostealer malware.
Cybersecurity analysts have confirmed that a massive trove of Gmail credentials has surfaced on underground forums, linked to widespread malware infections that quietly harvested login data over the past year.
The leaked information includes email addresses, passwords, and session tokens, potentially giving hackers unrestricted access to personal and corporate inboxes. Experts warn that the scope of this breach could surpass previous global leaks, urging users to act immediately to secure their Google accounts and linked services.
- 183 Million Credentials Exposed: A massive leak included Gmail accounts, sourced from phishing, malware, and past breaches—not a direct Google system hack.
- Password Reuse is Risky: Compromised credentials are exploited via credential stuffing, putting multiple accounts and digital identities at risk.
- Immediate Security Steps: Change Gmail passwords, enable 2-step verification, run Google Security Checkup, and stop password reuse across services.
- Businesses Must Act: Remote teams and enterprises should enforce unique passwords, 2SV, segmented Gmail use, and secure access tools like VPNs or dedicated IPs.
- Shift Beyond Passwords: AI-enhanced attacks make breaches inevitable; stronger authentication like passkeys, hardware tokens, and vigilant monitoring are essential.
What Exactly Happened in the Google Gmail Data Breach?
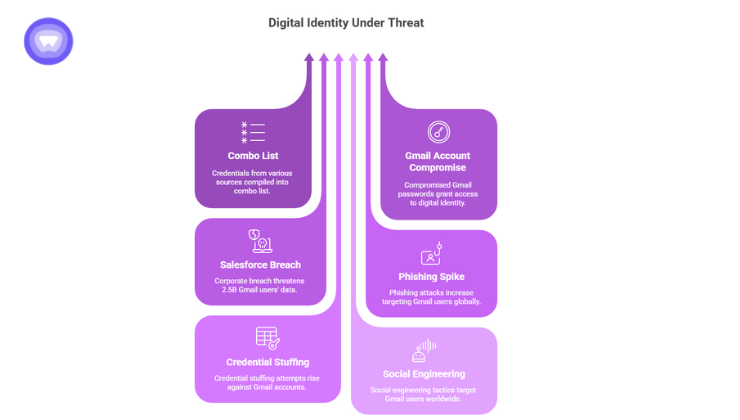
Reports indicate that roughly 183 million credentials, email addresses and passwords, have been exposed in what appears to be a massive aggregation of leaks and phishing yields.
- The data was not necessarily drawn from a direct breach of Google’s consumer systems; rather, it appears that credentials collected from multiple sources (phishing, device malware, older leaks) were compiled into a “combo list”.
- The leak is especially dangerous because many credentials include Gmail accounts, meaning a compromised password may give criminal actors access not just to email, but to a full digital identity via your Google gmail login.
- Notably, there has also been a separate incident reported: a corporate-level breach of a Google-managed Salesforce instance, prompting warnings that up to 2.5B gmail users at risk after a google data breach, though Google says consumer account credentials were not directly compromised.
- The cumulative effect: even if your Gmail password was not part of the initial 183 million, the news and related vulnerabilities have triggered a spike in phishing, credential stuffing, and social engineering targeting Gmail users globally.
Why the Google Gmail Data Breach Should Concern You
Your Gmail account is more than an inbox, it is the master key to your online identity. Password resets, bank alerts, cloud access, and account recovery all funnel through your Google Gmail login.
When passwords are reused, one leaked credential can unlock multiple systems. Attackers exploit this through credential stuffing, automated tools that test stolen email/password pairs against Gmail and other services to find active accounts.
The risks go far beyond unauthorized inbox access:
- Phishing escalation: Scammers now send fake alerts styled as “Google Gmail Data Breach Warning” emails, tricking users into clicking malicious links or “confirming” credentials.
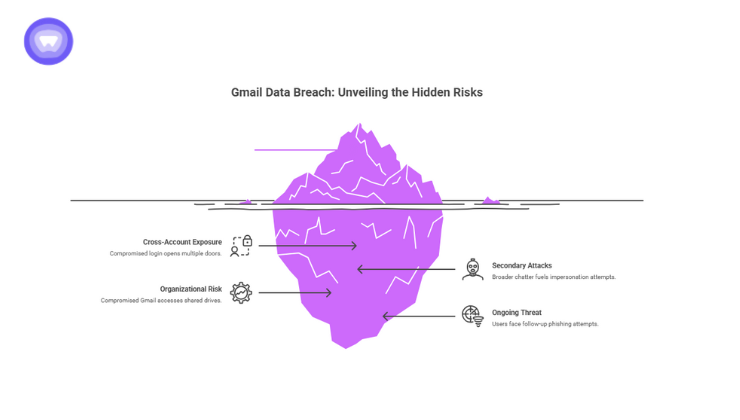
- Cross-account exposure: Many users link Gmail to cloud storage, payment services, and SaaS apps, a single compromised login opens multiple digital doors.
- Secondary attacks: Even if your address isn’t among the 183 million, the broader Google data breach chatter fuels impersonation, spoofing, and voice phishing (vishing) attempts.
- Organizational risk: For companies, one compromised business Gmail can give attackers access to shared drives, internal systems, and sensitive data.
- Ongoing threat: Reports warn that up to 2.5b Gmail users at risk after a Google data breach may face follow-up phishing and credential-reuse attempts.
Timeline and Key Numbers
The table below breaks down the key highlights of the breach.
| Metric | Detail |
| ~183 million | Number of exposed credentials in the main documented leak. |
| ~184 million | Another figure cited by multiple sources for similar credential dumps including Gmail, Microsoft, Apple accounts. |
| ~2.5B Gmail users at risk | This figure appears in reports following the Salesforce-linked Google breach, signalling the scale of potential exposure. |
| 47 GB | Approximate size of the exposed unencrypted database found by researcher Jeremiah Fowler, containing login details for Google and other services. |
| 16B credentials | Number cited in research for aggregated leaks globally in 2025 across multiple platforms, showing the broader context of password reuse risk. |
How This Breach Happened: Anatomy of the Attack
The Google Gmail Data Breach stems from infostealer malware that stole and exposed over 184 million credentials in an unsecured 47 GB database. While Google’s systems weren’t hacked, stolen logins from infected devices and third-party leaks put Google Gmail login details at risk through reuse.
Threat group ShinyHunters also used social engineering and fake “Google Gmail Data Breach Warning” emails to trick users into sharing codes. The result: massive credential stuffing attacks proving that reused passwords can turn any account into a vulnerability.
Google’s Response and What Users Need to Understand

Google confirms no direct breach of its consumer Gmail systems in the 183 million-credential leak segment. The exposed data mostly comes from external leaks or device-based malware.
- On the Salesforce breach, Google states that the data exposed was “basic and largely publicly available business information”, not consumer Gmail passwords, yet the resulting phishing risk is real.
- Google has issued advice and notifications to impacted business users, and prompted general security actions for Gmail users.
- However, Google also clarified that claims it emailed all Gmail users to reset passwords are false. Many outlets reported broad alerts; Google refuted that sweeping mass-notification occurred.
Google Gmail Data Breach: What Businesses Should Do Now
The Google Gmail Data Breach is more than a consumer threat, it’s a business risk. When Gmail logins are reused for SaaS tools, project management dashboards, or cloud storage, one compromised account can expose entire client ecosystems. For companies using Gmail across distributed or virtual teams, securing every Google Gmail login is now a top priority.
Here’s what businesses and IT teams should do under the “Google Gmail data breach what to do” checklist:
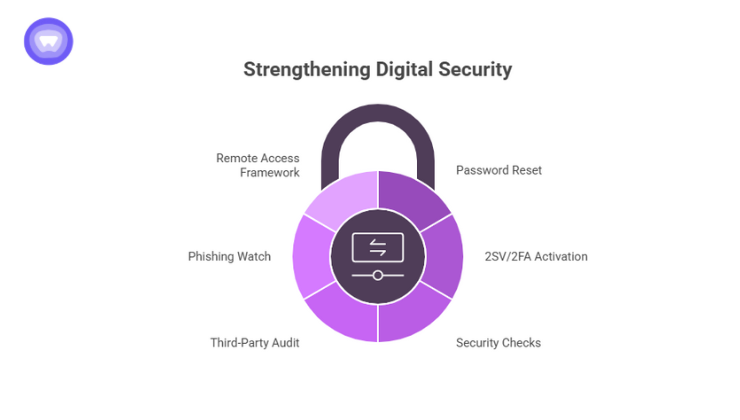
1. Enforce immediate password resets
- Require employees to change Gmail passwords and ensure each one is unique.
- Treat Gmail as a “master key” to internal and client systems.
- Use enterprise password managers to prevent reuse across multiple accounts.
2. Activate 2-Step Verification (2SV) or 2FA company-wide
- Use authenticator apps or hardware keys instead of SMS.
- For executives or client-facing users, enable passkeys for higher protection.
- Review recovery methods to ensure no shared or outdated backups.
3. Run account and device security checks
- Use Google’s Security Checkup to review connected apps, devices, and recovery details.
- Remove unknown integrations or inactive users.
- Deploy endpoint protection to detect infostealer malware on employee devices.
4. Audit third-party access and integrations
- Revoke unnecessary app permissions connected to Google accounts.
- Segment Gmail usage: separate admin, client, and personal accounts.
- Apply access control policies for shared drives and collaboration platforms.
5. Watch for phishing and impersonation attempts
- Alert teams to fake “Google Gmail Data Breach Warning” emails or calls from “Google Support.”
- Train employees to verify messages through official Google channels only.
- Reinforce zero-trust awareness, never share verification codes or passwords.
6. Strengthen your remote access framework
- Use identity-aware VPNs and secure tunnels for Gmail access within distributed teams.
- Monitor login locations and restrict access to approved regions or devices.
- Incorporate regular security hygiene reviews into onboarding and offboarding.
Gmail Account Protection Quick-Guide
Before panic sets in, take these rapid steps to secure your Gmail and prevent further damage, here’s your quick protection checklist:
| Step | Why It Matters | Action |
| Change Gmail password | Leak may include your credentials | Create unique passphrase; don’t reuse old password |
| Enable 2-step verification | Blocks login even if password is known | Use authenticator app or hardware key |
| Run Security Checkup | Detects hidden access & weak links | Remove unknown devices/apps; update recovery info |
| Check breach databases | Confirms if your data appeared in leak | Use trusted service; act if listed |
| Stop password reuse | Reuse is top risk driver in credential leaks | Use unique passwords everywhere |
| Be vigilant for phishing | Attackers now exploit breach news | Verify any “Google support” outreach independently |
| Secure devices & apps | Credentials often harvested from endpoints | Keep software updated; review app permissions |
Why This Event Is Different

Unlike a single company hack, the Google Gmail data breach is largely an aggregation of leaks, phishing yields and malware-harvested credentials.
That means the root cause is user behaviour (password reuse, device compromise) rather than a single platform vulnerability.
- The scale is enormous. With reports of 2.5 b gmail users at risk after a google data breach, the target base is massive, even if only a fraction of those accounts are directly exposed, many are indirectly vulnerable.
- Attackers are shifting: instead of targeting the service provider, they assault the identity layer, your Gmail login. This shift makes mitigation more about hygiene and less about vendor trust.
- The phishing system is now primed. Because of this event, you’ll see more “google gmail data breach warning” emails, more spoofed login pages, more speech-based social engineering (vishing).
Looking Ahead: The Broader Context
The Gmail breach is part of a much larger trend, researchers have uncovered over 16 billion login credentials leaked across major platforms like Google, Apple, Microsoft, Facebook, and even banking systems.
What’s changed is how this data is exploited: attackers now use AI-driven password testing, credential stuffing, and social engineering to breach accounts faster and more precisely. The age of relying solely on passwords is over. Stronger methods like passkeys, hardware tokens, and device-based authentication are becoming essential, and Google is already moving in that direction.
For both individuals and organizations, the mindset must shift, it’s no longer about if an account will be compromised, but when and how effectively you can respond.
How PureWL White Label VPN Solution Helps
In light of this, ensure your remote access and identity controls are up to date. A solution like PureWL White Label VPN Solution can complement your Gmail security efforts by encrypting traffic, enforcing device authentication and making sure that even if credentials are compromised, the attackers face an extra layer of protection.
Final Thoughts
The Google Gmail data breach is not just a news item, it is a moment to act. Your Gmail login might be safe in isolation, but repeated credentials, phishing campaigns and harvested device data mean that if you wait, your account may be next. Change your password, enable 2-step verification, monitor your account, educate your team, and treat this as a turning point in your digital security posture.


